Local Incentives Protocol
Decentralized Marketplace Infrastructure
by Qian Che and Daniel Olano · 2021
1. Introduction
Fiat money gives central banks huge control over the economy, an alerting thought since it is extensively used in all human trading activities. Risks have been observed in a number of countries as hyperinflation resulted from huge increases in the supply of paper money, e.g. currency instability in Venezuela that began in 2016. Since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, cryptocurrencies are not yet considered as mainstream currency in payment systems in exchange for common goods or services, e.g. a pizza, a painting, a house and so on. To fulfill this demand, Virto Network creates the Local Incentives Protocol(LIP) which defines a secure payment system and means to trade off-chain assets with cryptocurrency by connecting decentralized markets and users, LIP facilitates a better local welfare redistribution through local tax collection from economic activities.
Why? We live in a modern 21st century yet inequality still persists, whether in income, wealth, opportunities or other dimensions. Some of the most effective mechanisms governments have for reducing economic inequalities are taxes, cash and in-kind transfers. However these fiscal policies that help shape more equitable societies play a small role in low-income countries.
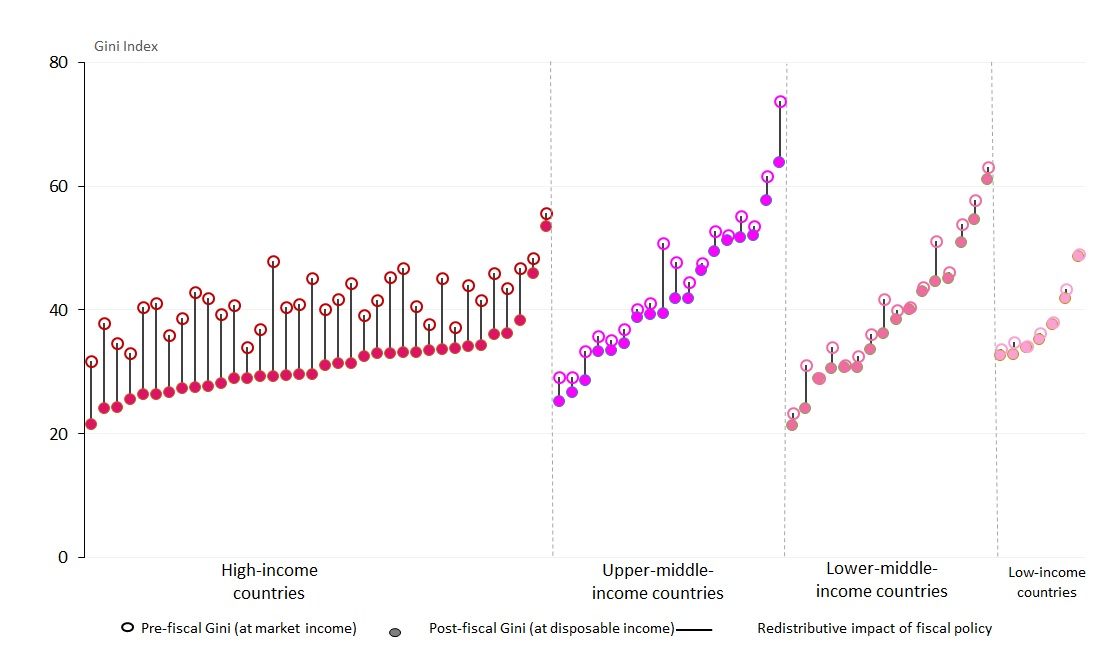
Through historical perspective, we observe the limitations of the current government taxing system to resolve economic inequality
- Fairness: Tributed local resources are managed by people with different interests
- Efficiency:Redundant intermediaries and bureaucratic bodies cost time and money
- Transparency: If people can’t track and feel the benefit of the spending process it lowers the trust in the system
Therefore we believe that LIP enables connected decentralized marketplaces to empower autonomous local communities by letting people and local communities be in control to collect and spend local tax in a fair, efficient and transparent way. Virto Network implements LIP as a token-less parachain in the Polkadot network providing Marketplace builders developer friendly API’s to easily build secure & highly scalable decentralized commerce applications so they can focus on solving the real problems.
2. Local Incentives Protocol
Local Incentives Protocol enables people to create stronger communities with aligned interests, to transact securely for goods and services in all kinds of decentralized marketplaces and to receive incentives through local tax collection to solve community problems in a fair, efficient and transparent way. All are enforced by blockchain technology.
2.1 Key actors
- Buyers/Customers: Anyone effortlessly joining the network in a trustless way that wants to buy goods or services from any other user.
- Sellers/Merchants: More experienced users trading their real world assets and services in exchange for cryptocurrency.
- Local community: People sharing a physical space who are incentivized to create communities and unlock existing and future resources which are collected from every trade with a local tax. Communities as DAOs decide to spend resources based on their needs to create powerful autonomous micro-economies
- Commercial community: People with a common interest in an economic activity create marketplaces that act like token curated registries where merchants post their products and services. They issue their own token used to bring value and utility to their community.
- Union: Communities and Marketplaces can together form unions, as a higher level DAOs to make decision to tackle global level topics.
2.2 Process
The world is divided into "Geo land cells". Each cell represents around 5 km2. When an individual creates an account, they register themselves in the cell of their choosing.
Individuals willing to exchange goods or services have two means of trading, peer-to-peer or via a commercial community.
- In P2P trading, people can freely trade as buyer and seller but are subject to a higher cost per transaction.
- When trading in in a commercial community, individuals apply to become qualified sellers or buyers that are subject to the higher quality standards of said community.
Therefore, individuals can freely trade with each other or in a regulated
marketplace run by the commercial community, both benefiting from the same
secure payment system embedded in the protocol, which
enables cryptocurrencies as payment method for service and off-chain assets.
Trading in a marketplace means the commercial community collects a market fee in
their native token as the cost of their service, which encourages new
commercial communities to join the system by creating applications to serve the demands
of the market.
Commercial communities also play a crucial role in the system as infrastructure
providers, with the collected fees they are expected to maintain a minimum
required server infrastructure to serve the market they wish to target, to
serve larger geographical and more densely populated areas, more infrastructure
and support from token holders is necessary, a mechanism that could incentivize
the creation of smaller markets instead of bigger ones.
For every trade within the system, a minimal system fee is charged to
secure the network and prevent abusive usage. Besides, a certain percent of the
traded amount is collected as local tax, which is directly locked in the Geo land
cells that could become future local communities. To form a community,
individuals from the same cell need to stake together enough resources passing a
threshold that indicates their willingness to form the community.
The system allows staking DOT tokens in local pools as they are the native
currency of the network to earn rewards coming from the Polkadot relay-chain as
well as getting rewards in land tokens.
Land tokens are unique non fungible assets that can be freely traded and
collected for use in local and system governance.
Due to the accumulated local tax, people are incentivized to create communities
with their peers, bonding assets to unlock existing and future resources that
are collected in the cells from trading activity. Besides, the system fee
collected also belongs to local communities. These communities will become DAOs
and decide to spend resources based on their needs to create powerful
autonomous micro-economies. Communities could decide about their own governance
system to better facilitate their economy in a dynamic way.
Local and commercial communities can also form unions, a permanent or temporary organization, to collectively solve bigger common goals. For example, all communities in the system can be part of a global union that collects funds to fight climate change.
2.3 Applications
To better serve their users, Commercial Communities often create their own decentralized
marketplace applications that connect to LIP for users to directly to interact with their
well curated listings.
All sorts of economic activities can take place in the marketplaces. The
following are reference applications developed by the core team as a showcase.
More applications are expected to be developed by other builders.
- Swap.cash: Decentralized on & off ramps, which enables an easy exchange between fiat money and cryptocurrencies
- Flea.market: P2P trade of local goods
- Go.delivery: Deliveries without intermediaries
3. Infrastructure
Local and Commercial communities are the main key entities in charge of providing infrastructure to the network, although anyone can run the necessary software to to participate, it becomes a requirement for them as they have the economic incentives to do so.
LIP distinct feature is to combine three different kinds of decentralized technology, a Substrate based parachain to be deployed in the Polkadot network, Matrix, the network for secure decentralization communications and Valor, an application runtime and development platform.
3.1 Parachain
A minimalistic blockchain runtime is used only for consensus critical functionality.
- Payments: The core functionality of the system, enables secure payments of off-chain assets with a highly configurable escrow-like system that protects users funds until the different parties have come to an agreement.
- Communities: DAO management tools that allow Unions, Local and Commercial communities take part in on-chain governance, treasury management, etc.
- Network assets: The parachain makes strong usage of inter-chain communication to allow merchants transact with all kinds of assets that might exist elsewhere.
3.2 Matrix
LIP uses the communications protocol in different ways,
- In the payment system it provides users with encrypted communication channels to exchange and store sensitive personal information.
- For key management and improved user experience, users can use their matrix account and familiar login facilities to interact with the blockchain.
- Marketplaces use specialized Matrix rooms and custom signed messages for merchant's listings.
- As general purpose message storage for non-consensus-critical data and as layer-two-like scaling platform, Matrix syncs data across a decentralized network of homeservers using rooms where only the involved parties need to store data.
3.3 Valor
A lightweight application runtime that allows composing community developed services that run in a community's infrastructure or fully decentralized in a user's device. One big focus of the runtime is to allow developers to use technologies the are already familiar with(e.g. HTTP based APIs) and have extensive support across all kinds of platforms. Due to the portability of the runtime and keeping applications' state in decentralized storages (i.e. blockchain, Matrix homeservers, IPFS), said APIs can be run unchanged in the user devices, including web browsers, making it an excellent Web 3 development environment.
4. Governance
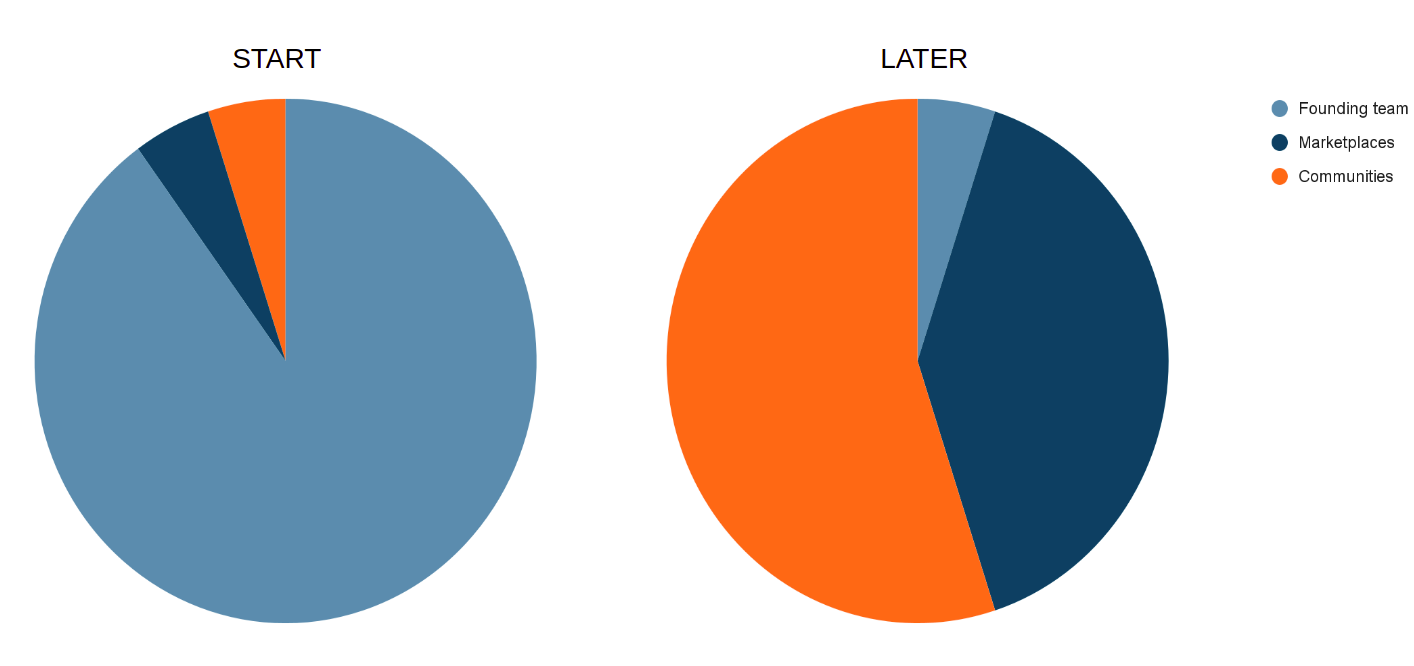
In its early days, LIP is governed mainly by the founding team which aims to function as a benevolent dictatorship to set up the initial system and maximize overall welfare and efficiency.
The more local and commercial communities are formed, each of them will form their own governance structure and achieve autonomy with a democratic and self-sufficient political economic system. Each community adopts their preferred democratic system based on different choices given by the protocol, being the one-person-one-vote system the default one. The global LIP system is governed by local and commercial communities as well as the founding that is programed to reduce its decision power gradually over time.
5. Economics
Different tokens are used across the system.
- Native Token: The parachain doesn't issue its own token, instead it uses Polkadot's DOT as native token, which follows Polkadot Network governance and distribution. We allow DOT staking via communities for participants to get rewards.
- Land Token: Land token is a form of hierarchical non-fungible "geo-token" within LIP representing land in the real world. Geo-tokens have different levels representing different varying sizes of land. Local communities are represented with geo-tokens starting at around 5 km2, derived from a H3(Hexagonal hierarchical geospatial indexing system) cell of level 7 resolution. The higher the level, the smaller the represented land size. The minimal unit of a geo-token that can be held and traded by a user is level 13 that represents around 43.9m2. The hierarchical nature of the token means a community(Lv7) holds around 117.6K of geo-token units.
- Marketplace Token: Each commercial community that connects to LIP can mint its own token for its operation. They also establish their own governance system and token economics. For every trade in a marketplace, the marketplace token is charged as the market fee and is converted from whichever currency was used for the trade, like a stable-coin, using a local decentralized exchange. A local tax that gets locked within the land cell for local communities to use.
5.1 Land Token
5.1.1 Key Functions
- Network Utility: Land token is a tradable NFT token that can be transfered across chains. and also utilized
- Local Governance: Land tokens can provide their holders voting rights at local community level and protocol wide voting power.
- Staking reward: Land tokens can be minted as reward for staking DOT.
- Community creation: Communities are created when enough land token holders within the community cell second the proposal for the community to be formed.
- Commercial community support: Land token holders can require deny or approve new businesses from operating in their geographical area.
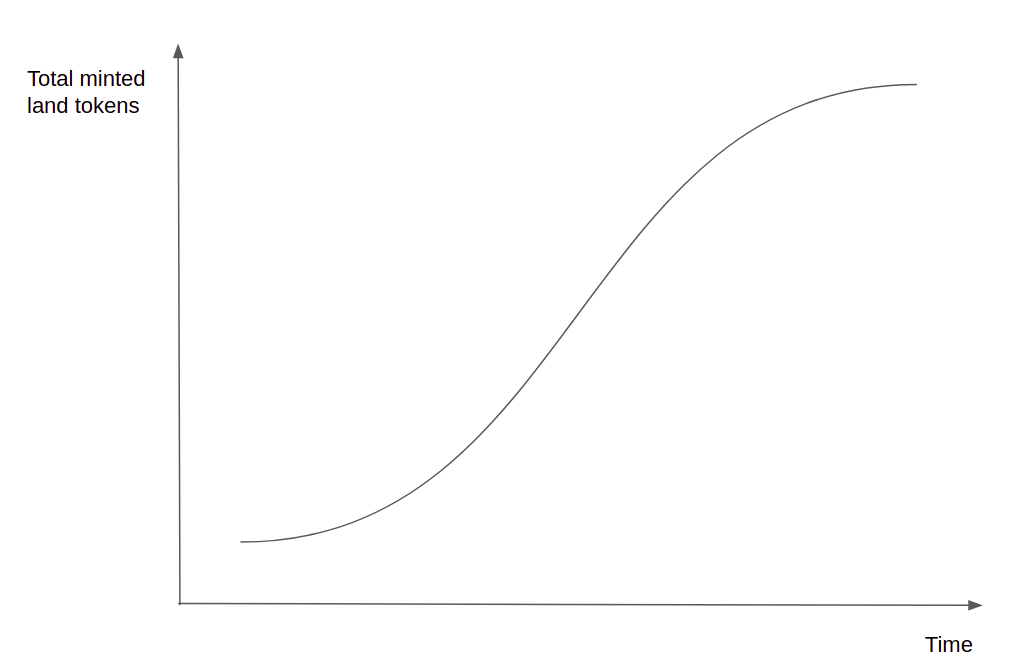
5.1.2 Minting and Distribution
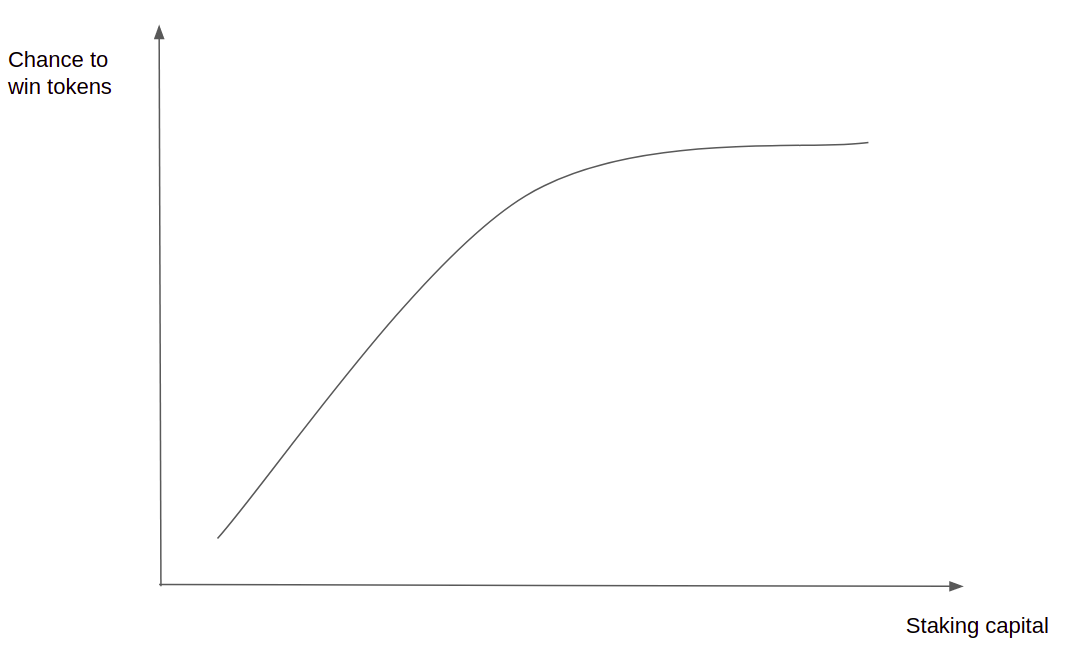
The total of 117.6K( =76) land tokens of each community is minted starting from time 0. The speed of token minting is rather slow in the beginning, then it speeds up to finally slow down as shown below. In each period, the total staking capital decides the chance for the individual to get the land token, usually staking higher capital means there is a higher chance of a reward until it reaches a certain threshold when the chance of winning no longer increases. The mechanism tries to increase fairness by preventing early birds and whales to take absolute advantage and monopoly the system's governance.
5.2 Marketplace Token
5.2.1 Key Functions
Marketplaces are free to decide how their token is used. Some examples are:
- Value accrual: Marketplace token is used to collect fees on every trade.
- Community Governance: As a governance token, marketplace tokens provide their holders voting rights within the community.
- Transparent marketing and growth: Commercial communities often allocate tokens to be used as rewards to attract more users into their platforms.
5.2.2 Minting and Distribution
Commercial communities are free to design their own token economics as they see fit with the condition that the system's governance controls their token's issuance, in the case of Virto Network the parachain will reserve minimum a 5% of a community's token allocation for itself so other actors in the system can participate in the community's governance and take decisions that benefit everyone in the system.
5.3 Launch on Polkadot as Parathread
Virto Network is the only planned implementation of LIP as we believe the
uniqueness of the Land Tokens should be kept(i.e. not two people should own
the same land in different systems). Also given its social impact and being
designed as a sustainable "token less" chain that inherits the relay chain
token(DOT) we believe there is place for the network to be considered a common
good chain.
As an alternative, Virto Network will operate as a Parathread paying for its
operation using the system fee until it can produce enough value to secure
a long-term parachain slot for itself in the future.